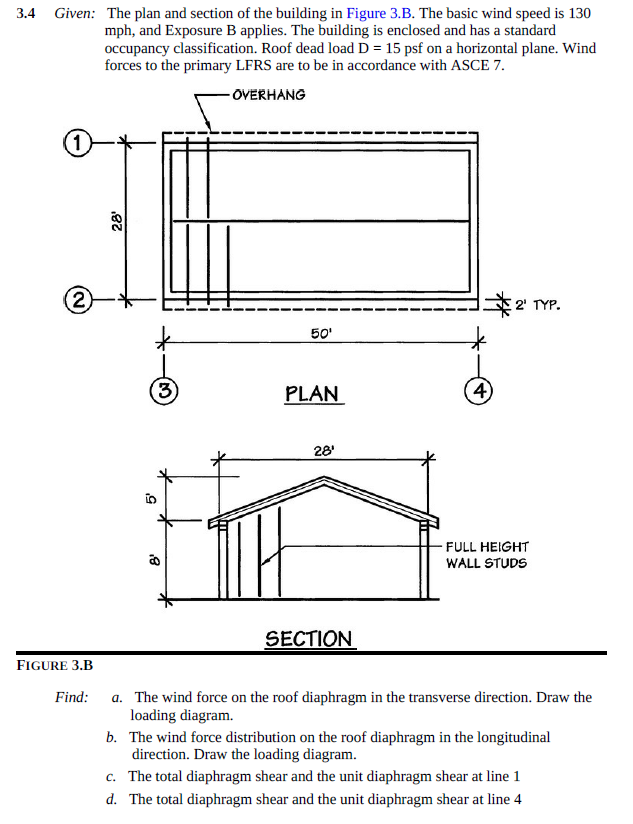
The basic design wind speed v mph corresponds to a 3 second gust speed at 33 above ground in exposure category c and is associated with an annual probability of 0 02 of being equalled or exceeded 50 year mean recurrence interval.
Wind force on roof in longitudnal direction.
Many studies on roofed structures have been performed in the past.
Studs are spaced 16 in.
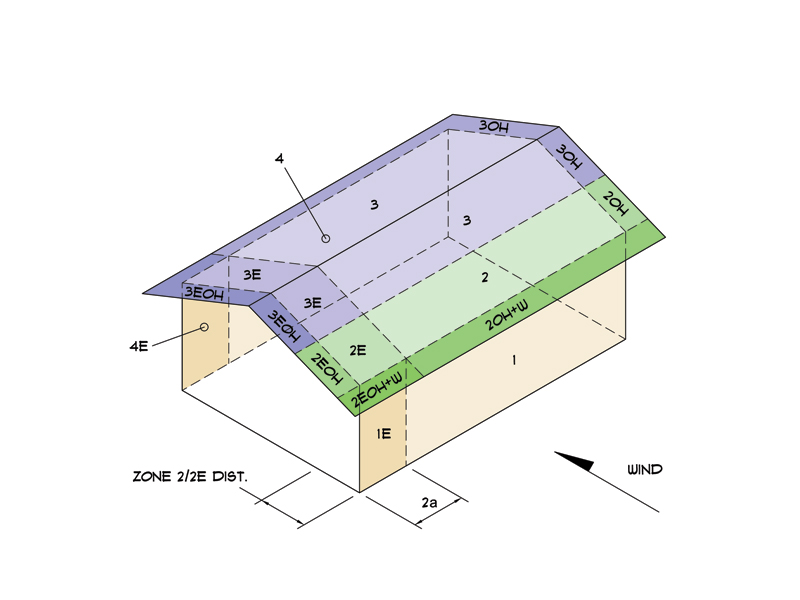
The remainder of zone 2 2e extending to the ridge line shall use the pressure coefficient gcpf for zone 3 3e.
For longitudinal load case the roof pressure coefficient gcpf when negative in zone 2 or 2e shall be applied in zone 2 2e for a distance from the edge of the roof equal to 0 5 times the horizontal dimension of the building parallel to the direction of the mwfrs being designed or 2 5 he at the windward wall whichever is less.
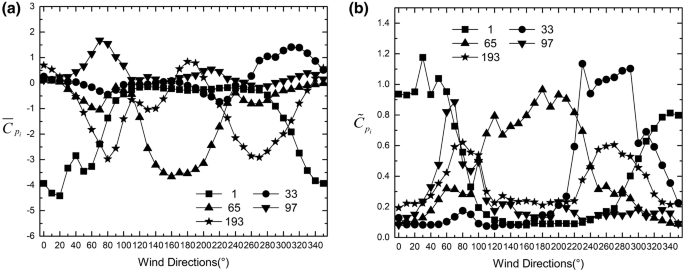
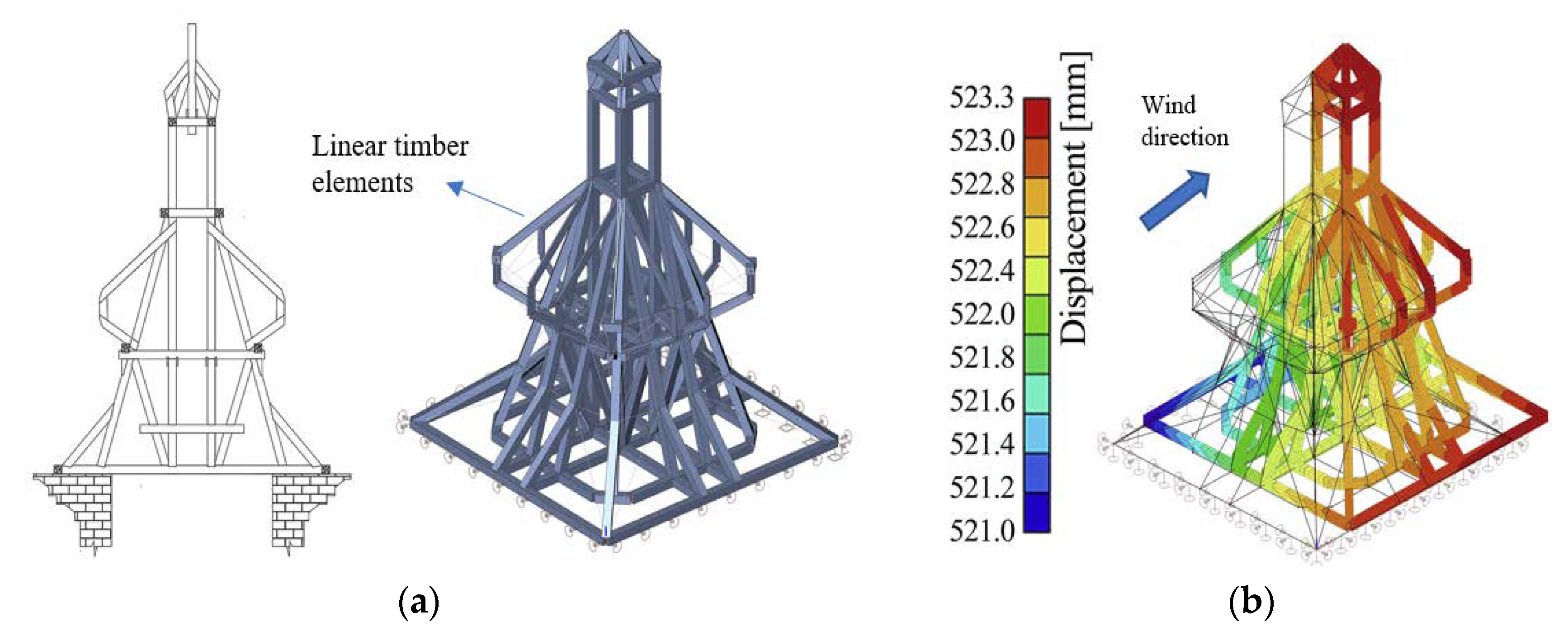
The present study demonstrates the pressure variations due to wind load on the pyramidal roof of a square plan low rise building with 15 wall openings through cfd computational fluid dynamics simulation.
The wind directionality factors k d for our structure are both equal to 0 85 since the building is the main wind force resisting system and also has components and cladding attached to the structure.
Wood structural panel sheathing is designed to function as a shearwall.
The critical lateral wind force in the longitudinal direction is given.
Since model scale wind tunnels typically use.
To calculate wind load using the generic formula use f a p cd where f is the force or wind load a is the projected area of the object p is the wind pressure and cd is the drag coefficient.
The same principle can be extended to any other structural member.
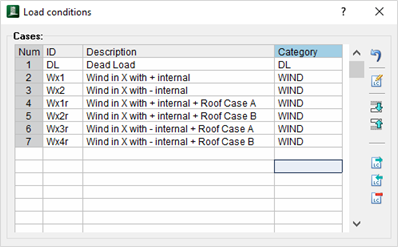
The load combinations for design are designated by the specific code required and are calculated and applied to the system in proportion to their mass.
Through which the force gets transferred to the next component girts.
First find a the area of the 2 dimensional face the wind is hitting using a length height for a flat wall.
In the longitudinal direction when the force acts on the gable ends of the building the first component to interact with the load is the cladding materials sheeting.
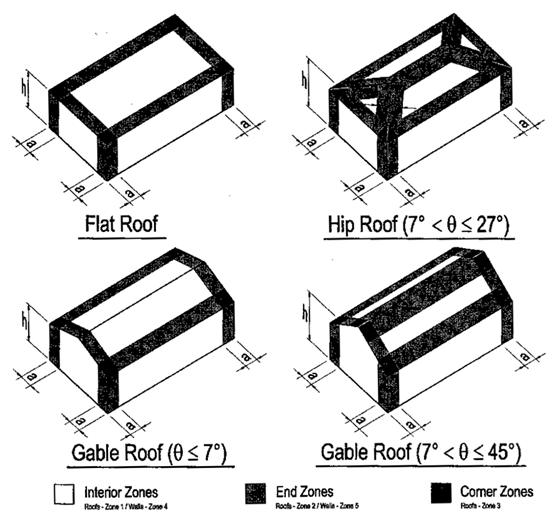
Roof shape and slope are both important parameters for the safety of a structure especially when facing wind loads.
The lateral and longitudinal force resisting system is comprised of a series of steel moment resisting frames roof and floor diaphragms and side wall shear panels the hrsg is designed as a three dimensional system comprised of these components.
6 1 see wind map webpage.
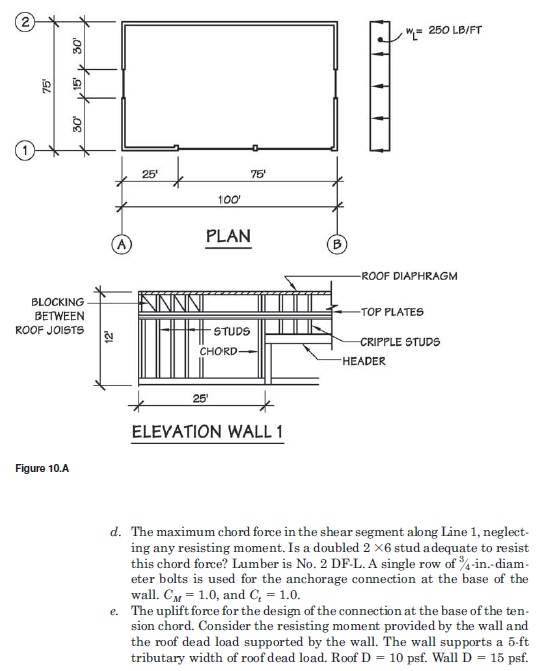
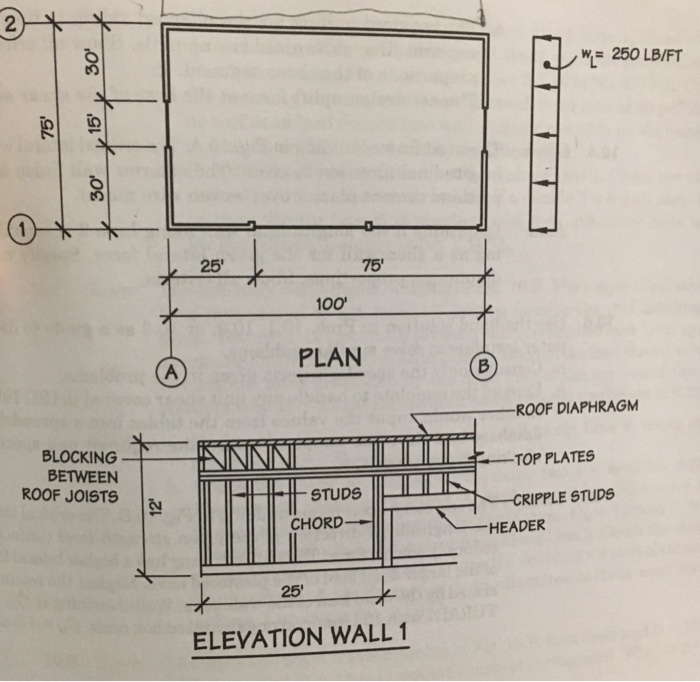
A find the unit shear in the shear segment along line 1 at the roof and 2nd floor level.
However the results suggest that modeling rme as a solid unit no venting leads to an overestimation of the forces in the vertical z direction.
For basic wind speed map fig.
Similarly wind load acting on the same column considering it as part of longitudinal frame perpendicular to transverse the wind load now acts in y direction and it s called longitudinal loading.