These example calculations assume transverse wind loads produce the controlling loading.
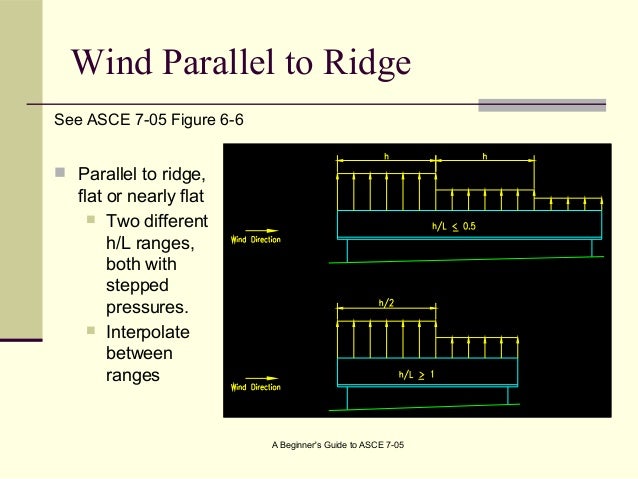
Wind loads direction parallel to ridge line or flat roof.
If you look at it simply as the direction that loads are acting then gravity loads are globally vertical and downward.
The remainder of zone 2 2e extending to the ridge line shall use the pressure coefficient gcpf for zone 3 3e.
Asce 7 05 protecting manufactured homes from floods and other hazards.
Generic building wind load dialog in all four cases a green arrow plays a crucial role in correct load generation in lean to and ridge roof the arrows are generated automatically by fd but for flat roof.
Minimum wind load for mwfrs design shall be 10 psf applied on projected vertical plane.
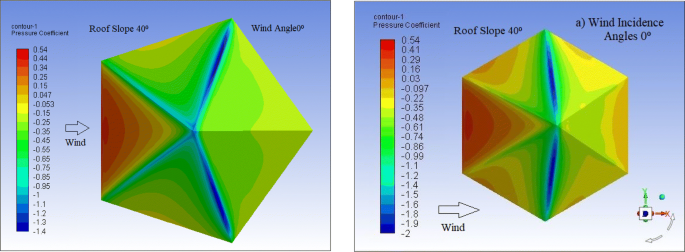
Face a is in the windward direction while face c is opposite to face a and is on the leeward side case 0 wind incidence angle.
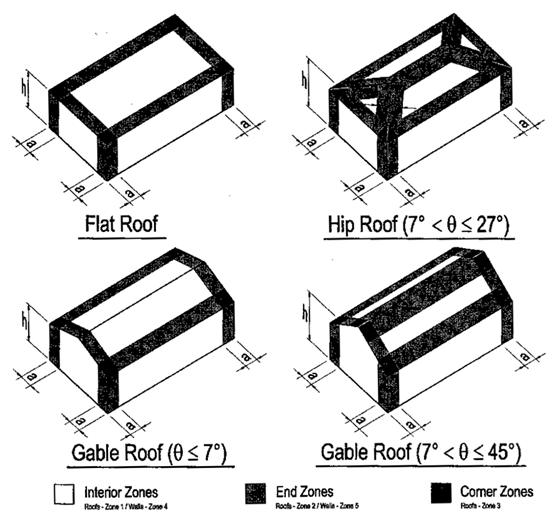
The roof has been divided into four parts i e.
Face a face b face c and face d.
Wind flow which denotes unobstructed wind flow with blockage less than or equal to 50.
External wall flat roof lean to or ridge roof.
Face b and face d are side faces of the roof and are parallel to wind flow when the wind incidence angle is 0.
For flat roofs roof angle 0 degrees either gable or monoslope may be used.
Generic building s wind load as surface loads can be placed automatically on covers.
Wind forces parallel to the ridge acting on the gable ends are liable to produce displacements and deformation of the roof trusses unless a thick gable masonry wall is provided at each end.
Wind parallel to ridge roof angle q for wind in longitudinal direction use q 0 degrees assumed.
When such end gable walls are not provided it is necessary to provide lateral bracings connecting the last two trusses.
90 degrees wind parallel to roof ridge.
This option allows to choose the wind direction for roofs as specified in asce 7 16 chapter 27 fig.
So say for a purlin design on a sloped roof gravity loads would cause bi axial bending in the purlin but pressure loads would cause only uni axial bending.
For calculating the sum of the wind load on the windward and leeward walls parallel to the building ridge the average roof height hr he 2 is used.
Pressures on roof surfaces parallel to the ridge windward roof cp 0 to h 2 varies 0 18 l h h 2 varies 0 18 0 5 h l 1 0 wind loads on non standard building configurations pressures on roof surfaces parallel to the ridge windward roof cp 0 to h 2 1 3 0 18.
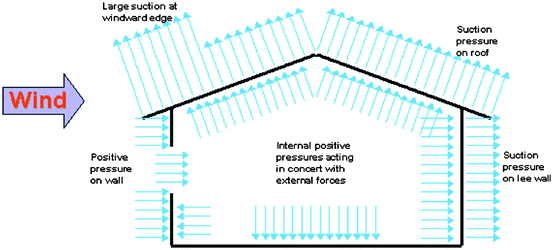
Pressures act normal to the surface.